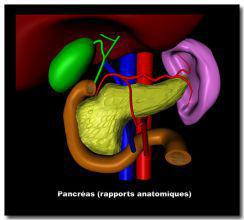
PANCREAS
Pancreatic cancer
Obstruction of the common bile duct by a malignant tumour causes jaundice. Pre-operative work-up consists of endoscopic ultrasound to evaluate the invasion of the tumour and biopsy sampling as well as lymph nodes mapping. Abdominal CT-scan is performed to assess local or distant metastatic lesions. In cases of advanced pancreatic cancer, radio-chemotherapy is advised before surgical resection. If the tumour is located in the head of the pancreas, a resection of the duodenum and head of the pancreas along with the gallbladder and distal part of the stomach is required. For tumours located in the body or tail, distal spleno-pancreatectomy is advised.
Pancreatic pseudocysts occur after episodes of acute pancreatitis. While small cysts do not need any treatment, larger ones may require either endoscopic gastric drainage if possible, others require drainage under CT-scan guidance. In selected cases, surgical drainage may be necessary.
Serous or mucinous cystic lesions of the pancreas occur in 10% of the cases. CT-scan and pancreatic MRI allow a characterization of the lesion. Endosonography is advised to obtain fluid for cytology examination and dosage of CEA and CA 19-9 tumor markers. Size and location of the cyst, its connexion with/without the pancreatic duct, the morphologic appearance of pancreas tissue are key elements to diagnosis. If intraepithelial pancreatic mucinous neoplasia (IPMN) with pancreatic duct involvement is diagnosed, surgical resection is advised as well as in cases of mucinous cystoadenoma. Serous cystoadenoma does not require surgery.
Left robotic pancreatectomy with spleen preserving
12, Chemin de Beau Solleil, 1206 Geneva- Switzerland – Ph. +41 22 786 32 92